VACC
The Voice Assistant Conversation Corpus
Related Paper: Siegert, Ingo; Krüger, Julia; Egorow, Olga; Nietzold, Jannik; Heinemann, Ralph; Lotz, Alicia Flores Voice Assistant Conversation Corpus (VACC) - a multi-scenario dataset for addressee detection in human-computer-interaction using Amazon's ALEXA In: Proceedings of the LREC 2018 Workshop LB-ILR2018 and MMC2018 Joint Workshop, 7 May 2018, Miyazaki, Japan - Paris, ELRA, p. 51-54
Brief Information
Collected Data
Recording Setup
Content of the Corpus
Participant's characterization
Related Publications
Brief Information
The Voice Assistant Conversatio Corpus (VACC) is a new type of conversation corpus in the field of human-computer interaction. It was created in collaboration with the Cognitive Systems Group and the University Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy.
The main goal of the data set is to enable studies on human-machine interaction. The aim was to vary certain boundary conditions:
- The type of dialog (formal, informal)
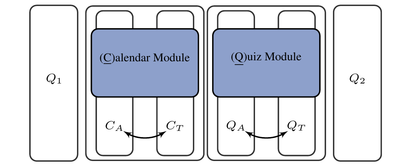
- The number of interaction partners (human-machine vs. human-human-machine) The interaction was conducted using a commercial language assistance system (Amazon's ALEXA). The participant was given two different tasks, one after the other. First, dates for exercises have to be determined, whereby the participant's calendar can only be requested via ALEXA. Then quiz questions have to be solved with the help of ALEXA.
Both tasks are performed once alone and once together with an interaction partner. This partner only interacts with the test person and not with ALEXA.
Collected Data
- Audio recordings
- from the participant
- from the interlocutor and
- from the overall scene
- Questionnaires
- Socio-demographic information (before the experiment)
- Experiences with technical systems in general (before the experiment)
- Perception of ALEXA and the interlocutor (after the experiment)
- Changes in voice and speech behavior during interaction (after experiment)
Recording Setup
The recordings took place at the Institute of Information and Communication Engineering. They were conducted in a living-room-like surrounding. The aim of this setting was to enable the participant to get into a natural communication atmosphere (in contrast to the distraction of laboratory surroundings).
As voice assistant system, we used the Amazon ALEXA Echo Dot (2nd generation). We opted for a commercial system to allow a fully free interaction with a currently available system.
The recordings were conducted using two high-quality neckband microphones (Sennheiser HSP 2-EW-3) to capture the voices of the participant and the interlocutor as well as one high-quality shotgun microphone (Sennheiser ME 66) to capture the overall acoustic scene and especially the output of the voice assistant. The recordings were stored uncompressed in WAV-format with 44.1 kHz sample rate and 16 bit resolution.
Content of the Corpus
| Participants | 27 German-speaking students |
| Distribution of Sex | 13 men 14 women |
| Distribution of Age | MW 24 years STD 3.32 years Min: 20, Max: 32 years |
| Total amount of data | 17 hours |
| Mean duration per dialog | 31 minutes |
| Annotation | utterances, type of utterances, transcripts, laughter, discourse particles |
| Collected Questionnaires | evaluation of interaction and speaking style, experiences in interacting with voice assistants, socio-demographic data, AttrakDiff |
Participant's characterization
The participants came from different study courses including computer science, engineering science and humanities. Thus, this dataset is not biased towards technophilic stu- dents.
Regarding the experience with ALEXA, all participants had known Amazon ALEXA before. When asked about experience with ALEXA, only six participants specified that they had used ALEXA prior to this experiment. Five of them used ALEXA rarely for testing, only one participant specified that he uses ALEXA regularly – for playing music.
When asked about the experience with other voice assistants, additional ten participants indicated prior use. As voice assistants, they indicated Apple SIRI, GOOGLE NOW, or Microsoft CORTANA. Seven of them used these voice assistants seldom, just to try. Only three used them regularly, e.g. for programming a timer. In total, 18 out of 27 participants have prior experience with voice assistants.
The nine participants not using any voice assistant before mistrusted the necessity of voice control and expressed data protection concerns when asked for reasons.
Related Publications
Siegert, Ingo; Sinha, Yamini; Jokisch, Oliver; Wendemuth, Andreas Recognition performance of selected speech recognition APIs - a longitudinal study In: Speech and Computer: 22nd International Conference, SPECOM 2020, St. Petersburg, Russia, October 7-9, 2020, proceedings - Cham: Springer; Karpov, Alexey . - 2020, S. 520-529 - ( Lecture notes in computer science; 12335)
Siegert, Ingo; Krüger Julia HOW DO WE SPEAK WITH ALEXA - SUBJECTIVE AND OBJECTIVE ASSESSMENTS OF CHANGES IN SPEAKING STYLE BETWEEN HC AND HH CONVERSATIONS, In: Kognitive Systeme- Duisburg: DuEPublico, 2013, 1, insges. 11 S., 2018
Raveh, Eran; Steiner, Ingmar; Siegert, Ingo; Gessinger, Iona; Möbius, Bernd Comparing phonetic changes in computer-directed and human-directed speech In: Elektronische Sprachsignalverarbeitung 2019 - Dresden: TUDpress, S. 42-49 - (Studientexte zur Sprachkommunikation; 93) ; [Konferenz: 30. Konferenz Elektronische Sprachsignalverarbeitung 2019, Dresden, 6.-8. März 2019]
Akhtiamov, Oleg; Siegert, Ingo; Karpov, Alexey; Minker, Wolfgang Cross-corpus data augmentation for acoustic addressee detection In: 20th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue - Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), S. 274-283, 2019 ; [Tagung: 20th Annual Meeting of theSpecial Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue,SIGDIAL 2019, Stockholm, Sweden, 11-13 September 2019]
Raveh, Eran; Siegert, Ingo; Steiner, Ingmar; Gessinger, Iona; Möbius, Bernd Three is a crowd? - effects of a second human on vocal accommodation with a voice assistant In: Interspeech 2019 - International Speech and Communication Association, S. 4005-4009
